Understanding External Rotation Shoulder Degrees: A Comprehensive Guide
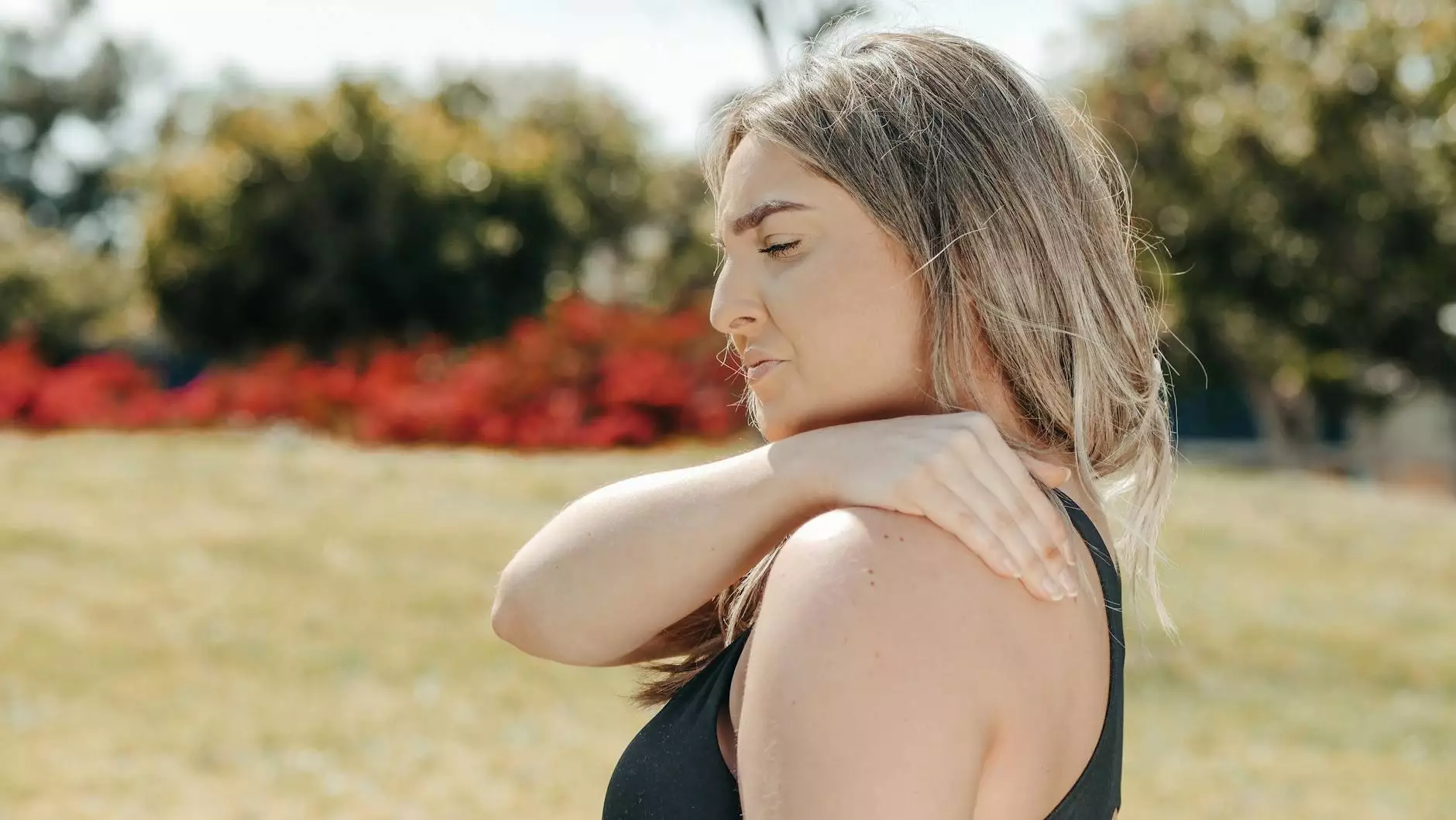

Introduction to Shoulder Mobility
The shoulder joint is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the human body, allowing for a remarkable range of motion. Understanding how the shoulder operates and the significance of actions like external rotation is essential for anyone involved in sports, physical therapy, or general health. This article will explore external rotation shoulder degrees, their relevance in health and fitness, and practical tips for improvement.
What is External Rotation of the Shoulder?
External rotation of the shoulder refers to the movement where the arm is rotated away from the body. This movement is crucial for various daily activities and athletic performances. When you lift your arm and turn your hand outward, you engage in external rotation. Understanding the degrees of this movement can provide significant insights into shoulder health.
Importance of Measuring External Rotation Shoulder Degrees
Measuring external rotation shoulder degrees is more than just a clinical assessment; it's fundamental for diagnosing potential issues and guiding rehabilitation protocols. Here's why it matters:
- Injury Prevention: Knowing your range of motion helps identify potential weaknesses that could lead to injuries.
- Rehabilitation: Accurately measuring rotation can help track progress during recovery from shoulder injuries.
- Performance Optimization: Athletes can enhance their performance by understanding the mechanics of shoulder movements.
How to Measure External Rotation Shoulder Degrees
Measuring external rotation can be done using a goniometer, a common tool in physical therapy. Here’s how to effectively measure external rotation shoulder degrees:
- Preparation: Ensure the person being measured is comfortable, seated, or standing with good posture.
- Positioning: The arm to be measured should be raised to 90 degrees in the plane of the scapula (shoulder blade).
- Measurement: Place the goniometer’s stationary arm parallel to the torso and the movable arm aligned with the forearm. Record the angle when the forearm is rotated away from the body.
- Comparison: Repeat the measurement on both sides to identify any discrepancies.
Normal Ranges for External Rotation Shoulder Degrees
The standard range for external rotation shoulder degrees varies based on several factors, including age, sex, and activity level. However, generally, the following guidelines apply:
- Healthy Adults: 80 to 90 degrees of external rotation is typical.
- Athletes: May exhibit greater external rotation due to increased flexibility and training.
- Age Considerations: As age increases, natural degradation can lead to decreased range of motion.
Common Issues Related to External Rotation
When external rotation is limited, it can lead to a variety of problems, including:
- Impingement Syndrome: Compression of shoulder tendons can lead to pain and limited mobility.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: The rotator cuff can become injured, leading to pain and decreased range of motion.
- Frozen Shoulder: Adhesive capsulitis can restrict movement, including external rotation.
Benefits of Improving External Rotation
Enhancing your external rotation can provide numerous benefits:
- Increased Functionality: Improved range of motion allows for better performance in sports and daily tasks.
- Reduction of Pain: Greater mobility can alleviate discomfort associated with restriction.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Athletes can achieve greater efficiency in movement patterns.
Exercises to Enhance External Rotation
Incorporating specific exercises can significantly improve external rotation. Here are a few recommendations:
1. Band External Rotations
Using a resistance band, this exercise involves twisting your arm outward while keeping your elbow tucked in. This movement strengthens the rotator cuff.
2. Side Lying External Rotations
Lying on your side with the arm above the elbow, rotate the forearm up towards the ceiling. This exercise targets the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles.
3. Wall Angels
Standing against a wall, keep your arms bent at 90 degrees. Slide your arms up and down, maintaining contact with the wall. This promotes shoulder mobility and stability.
The Role of Physical Therapists and Chiropractors
Healthcare professionals, especially physical therapists and chiropractors, play a crucial role in assessing and improving external rotation shoulder degrees. They can offer personalized treatment plans that may include:
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques can improve mobility and alleviate pain.
- Customized Exercise Regimens: Tailored programs to enhance strength and flexibility.
- Education and Awareness: Helping patients understand their conditions and the importance of shoulder health.
Conclusion
Understanding and improving external rotation shoulder degrees is essential for everyone, from athletes to individuals managing chronic shoulder pain. By regularly measuring your shoulder's external rotation, practicing specific exercises, and seeking professional guidance, you can enhance your shoulder health and overall quality of life. Remember, taking proactive steps towards shoulder mobility can make a significant difference in your physical capabilities and well-being.
For more information about shoulder health and related topics, visit IAOM-US.